Homepage › Forums › Articles › Operating Systems › Linux › Privacy and Linux
Tagged: compress, encryption, linux, lock, privacy, proxy, steganography
This topic was published by DevynCJohnson and viewed 2200 times since "". The last page revision was "".
- AuthorPosts
Linux is a very secure system, but maybe you want more privacy. Even though Linux is very secure, users can take extra precautions for more privacy. Maybe you work for a very large company and want to ensure that particular files are not easily accessed. Maybe you keep your diary on your computer (bad idea but some people still do it) and you want additional security for that particular file. Well, this is the article for you.
Locking Compressed Files
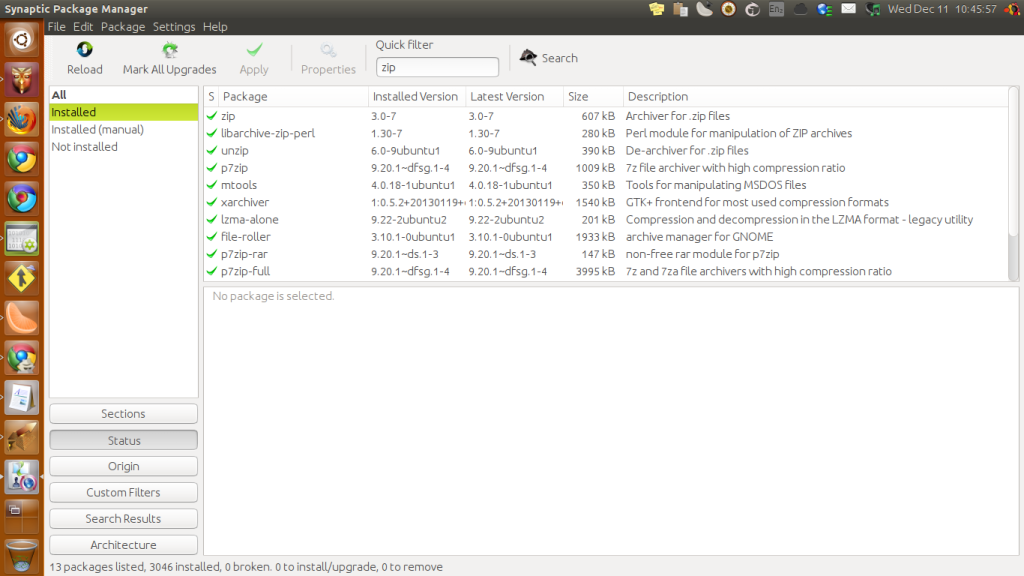
One obvious and easy way to protect files is by compressing them using a compression algorithm that supports password protection/locking. Many compression/archive applications exist for Linux. The one that I highly recommend for most Linux systems is "Archive Manager". To get support for some of the compression formats I am about to suggest, you may need to install some special libraries and packages like "zip", "libunrar0", "p7zip-*", "rar", etc.

Install Zip NOTE: Some of these compression formats (like RAR) are non-open-source software.
Some examples of compression formats with password protection abilities include 7z, arj, cbr, cbz, exe, rar, and zip (others may exist). I have "Archive Manager" installed on my system and many compression libraries.

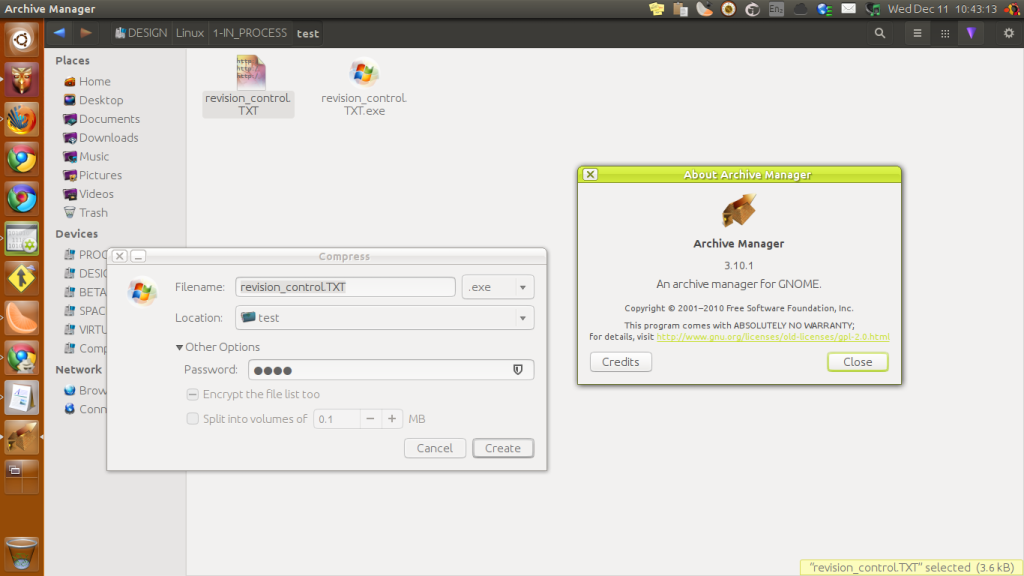
Lock Archive Depending on what compression/archive software you prefer, compress your file using one of the suggested formats and make a password. Once the file is created, make sure it has successfully locked and that the password works before you delete the uncompressed file.
For extra privacy, compress as an "EXE". This makes the file appear as an executable. Who would expect it to be a compressed PDF with a company's secret plans? For even more privacy, after compression (what ever format you choose), rename the file extension to ".ko" and (with Root privileges) place the file somewhere in /lib/. No one would ever try (or want) to open each library file with a compression utility hoping to find secret files.
Web Browser Privacy
Obviously, remember to clear/delete your cache and history. Alternately, set up the browser to not keep history or any other temporary files.
Some add-ons for Firefox offer extra privacy tools and features. Check out https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/extensions/privacy-security/ to get some privacy addons for Firefox.
Tor can help protect your identity while you surf the Internet. Setting up Tor is a subject all its own, but here are some links to get started with Tor:
- Tor: Part 1 - http://www.linux.org/threads/tor-part-1-is-it-for-me.4532/
- Tor: Part 2 - http://www.linux.org/threads/tor-part-2-installing-and-using.4533/
- Tor: Part 3 - http://www.linux.org/threads/tor-part-3-becoming-an-onion.4543/
Proxy Server
Individual web browsers can be set up to use proxy instead of the whole system. For some browsers, the proxy settings can be set in the options. Some browsers require a special addon to handle proxies itself rather than the system as a whole. Chrome and Chromium can use "Falcon Proxy" to utilize the benefits of proxies. Firefox can use "FoxyProxy" or "One Click Proxy IP". Other addons exist for these browsers, so do some research to find the one that best suits your needs. To find a list of proxy servers, go to hidemyass.com.
Encryption
Make an encrypted partition to store files that most people should not see. Or, encrypt a directory. Instructions on encrypting partitions, filesystems, and directories is out of the scope of this article.
Steganography
Files can be hidden in other files. For example, compress some of your files using zip and then get a JPEG that will be used to hold the zip. Use the command
cat IMAGE.jpg HIDE.zip > SOME_PIC.jpg. The image file "SOME_PIC.jpg" will appear as a typical and viewable image. To retrieve the zip, use the commandunzip SOME_PIC.jpg.To test the possibility of an image containing a zip, use this command - "unzip -t IMAGE.jpg". If the output contains information about "extra bytes at beginning or within zipfile", then the file most likely contains a file.
Divide
A compressed file (or any file) can be divided into multiple files. If the split file is an image, then the image cannot be viewed. Also, each piece can be hidden in another file if needed. To split/divide a file, use this command - "split --number=NUM ./FILE" where "NUM" is the number of pieces to make and "FILE" is the file to be split. The pieces will be titled "xaa", "xab", "xac", "xad", "xae", ...... To put the pieces back together, use this command with the files/pieces list alphabetically - "cat ./xaa ./xab > ./NEW_FILE".
Further Reading
- DarkWeb Link List - https://dcjtech.info/topic/darkweb-link-list/
- General Tor Info - http://lifehacker.com/what-is-tor-and-should-i-use-it-1527891029
- Electronic Frontier Foundation - https://www.eff.org/
- OpenNet Initiative - https://opennet.net/
- Info on the NSA's illegal mass surveillance program - https://www.eff.org/nsa-spying
- AuthorPosts